 |
| February 07, 2012 | Volume 08 Issue 05 |
Designfax weekly eMagazine
Archives
Partners
Manufacturing Center
Product Spotlight
Modern Applications News
Metalworking Ideas For
Today's Job Shops
Tooling and Production
Strategies for large
metalworking plants
Eccospheres aim to prove their heat-shielding mettle on Mars mission

Glass microspheres from Trelleborg Offshore were specified by Lockheed Martin for use in the composite aeroshell system of the recently launched MSL Curiosity Rover.
High-performance glass microspheres from Trelleborg Offshore were specified by Lockheed Martin for use in the composite aeroshell system used to protect the car-size Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) Curiosity rover launched November 26, 2011 from Cape Canaveral, FL.
Designed and built by Lockheed Martin Space Systems, the aeroshell is a blunt-nosed cone that encapsulates and protects the Curiosity rover during its deep-space cruise to Mars, and from the intense heat and friction that will be generated as the system descends through the Martian atmosphere. The capsule, which was launched by NASA, measures 15 ft (4.5 m) in diameter, the largest to date, and includes a composite load-carrying structure as well as a thermal protection system.
The Eccospheres and NASA go way back. "Due to their high thermal resistance and lightweight, customizable properties, Trelleborg Eccospheres have served as a critical raw material component utilized in ablator, insulation, and adhesive systems for spacecraft design since the dawn of the U.S. space program," says Will Ricci, aerospace sales manager, Trelleborg Offshore. "We were a critical supplier to the NASA space shuttle program.
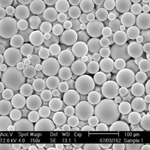
"With the Mars Science Laboratory the most ambitious Mars mission to date, it was imperative that the aeroshell was designed and built to withstand the demanding Martian atmosphere, without fail. As such, Lockheed Martin decided to make Trelleborg's Eccosphere glass microspheres a part of their mission-critical backshell thermal protection system."
Lockheed Martin provided the aeroshell to NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the MSL mission and designed and built the Curiosity rover. MSL has the scientific goals of determining if the planet was ever habitable, characterizing the climate and geology of Mars, and preparing for human exploration.
"The aeroshell is a vital part of the mission, forming a protective covering for the rover during the eight-month voyage to Mars," says Rich Hund, MSL Aeroshell program manager at Lockheed Martin. "Its main purpose is to protect the rover and descent stage from the intense heating of entry through the thin Martian atmosphere on landing day, ensuring it can complete its important mission."
The aeroshell is composed of a two-part system: the front-facing heatshield is a phenolic impregnated carbon ablator (PICA) designed to take the brunt of the Martian re-entry, while the backshell has a super-lightweight ablator (SLA0561V) material containing the Trelleborg Eccospheres as one of the ingredients. The SLA-561V ablator has flown on all of NASA's previous Mars entry vehicles.
Trelleborg Offshore's glass Eccospheres are hollow thin-walled microspheres composed of sodium-depleted borosilicate glass. To the naked eye, they resemble a fine, white, free-flowing powder, but magnification reveals them to be near-perfect spheres. They are designed to help reduce costs, enhance properties, and improve processability.
The exclusive glass chemistry and proprietary manufacturing techniques of Trelleborg's Eccospheres produce a product that features highly chemically inert sodium-depleted glass and exhibits superior thermal performance with material integrity up to 900°C/1,652°F. The Eccospheres also have low resin interaction when compared to other glass fillers. The removal of residual broken material and highly regular particle geometry result in industry-leading strength/weight ratios, while being capable of extremely high loadings in liquid resins. Additionally, Eccospheres glass microspheres allow for maximum versatility in composite formulations due to their low impact on resin viscosity and non-interacting chemical purity.
SIDEBAR: Typical uses for Eccospheres
Eccospheres glass microspheres are used extensively throughout the aerospace industry and are specifically engineered to provide product solutions. Key properties such as low density/high strength, low thermal conductivity, and high heat resistance are all essential in the following applications:
- Void fillers: For lightweight composites;
- Edge sealers: Prevention of water ingress;
- Ablative coatings: Heat shield of rockets, space vehicles, and missiles;
- Potting compounds: Encapsulation of electronic components;
- Abradable seals: Used in jet engines to improve efficiency;
- Radomes: Lightweight and RF transparent;
- Specialty paints and coatings: Stealth technology;
- Core fillers: For weight reduction of turbine blades.
In addition to offering a standard range of Eccospheres glass microspheres, Trelleborg can customize microspheres according to customer specifications by modifying the starting materials and manufacturing parameters. This allows the manufacturer to control characteristics such as density, strength, particle size, and packing factor. If required, various surface treatments such as silanes can be applied.
More recently, the company's ability to coat microspheres has extended to the use of metallic compounds. Such products are developed for the manufacture of specialty paints and coatings and can offer the following properties:
- Magnetism;
- Radar (and other EM) absorption or reflection;
- Pigmentation;
- Electrical and/or heat conduction.
Eccospheres glass microspheres are used in a variety of applications in the marine surface sector, such as caulks and putties, deck-leveling compounds, anti-fouling paint, and syntactic in-fill material. New areas of development include the use of microspheres in lightweight passive radar systems and specialty paints for signature management, via the use of various metallic surface treatments on the microspheres.
Customizing Eccospheres glass microspheres has also resulted in the development of a new generation of "binary microspheres" that have an improved packing factor as well as low density and high strength. Binary microspheres have significantly improved the performance of syntactic foams used in deep-water buoyancy applications. Other applications include neutral-density cable sheaths for towed array systems and lightweight, RF transparent radomes for submarines.
Because of their energy-absorbing properties, both microspheres and macrospheres are also used in many blast-protection systems. Trelleborg's unique ability to produce dye-filled macrospheres has resulted in their use in a "bruisable composite," where damage can be easily identified after impact.
Want more information? Click below or email tec.sales@trelleborg.com.
Rate this article
View our terms of use and privacy policy
